- New Sublingual Allergy Tablets - October 31, 2014
- Ground-breaking New Treatment Option for Sleep Apnea - September 27, 2014
- Allergies versus Viruses in Children - September 27, 2014
- “Dog Dust” Protects Children from Allergies - September 27, 2014
- Nasal Saline Irrigation - August 8, 2014
- Doctor, I am Allergic to Dust. What Can I do? - July 31, 2014
- Infants Exposed to Dust Mites Less Likely to Develop Allergies - June 23, 2014
- How to Treat a Young Child’s Cough - December 17, 2013
- Many Parents are Unaware That Their Children Are at Risk for Noise Induced Hearing Loss - December 9, 2013
- Is it a Cold or an Ear Infection? - December 9, 2013
 It is often the subject of a family joke when a child snores. A parent will often tease that they can hear their child from the other room. However, while it is often of no clinical concern, sometimes snoring in children is a real medical issue.
It is often the subject of a family joke when a child snores. A parent will often tease that they can hear their child from the other room. However, while it is often of no clinical concern, sometimes snoring in children is a real medical issue.
10% of children are known to snore. But sometimes this goes beyond snoring alone. Sometimes, the child actually stops breathing occasionally. This is called obstructive sleep apnea.
What is obstructive sleep apnea?
Obstuctive sleep apnea (OSA) is a sleep disorder that can occur in children or adults. It is diagnosed when there are respiratory pauses (periods where the person stops breathing) while sleeping. This results in gasping, choking and restless sleep.
Why does obstructive sleep apnea occur?
There are many reasons for OSA to occur. The reasons are often quite different in adults, versus in children. In children, the most common contributors of OSA in children are:
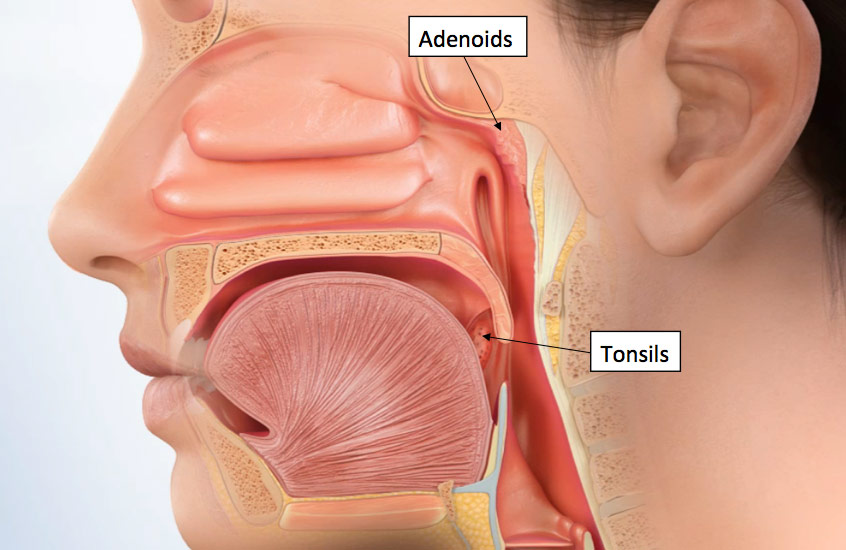
- Enlarged tonsils
- Enlarged adenoids
- Craniofacial abnormalities (atypical bones/skeleton of the face and neck)
- Obesity
- Allergies/asthma
How can I tell if my child is just snoring or if they have real OSA?

It is not always easy for a parent to be able to tell the difference between simple snoring and true obstructive sleep apnea. However, the clearest sign is the child who will snore and then stop snoring for a few seconds, gasp or snort, and then resume snoring. The pause in snoring is actually a pause in breathing and is very typical of sleep apnea. Other symptoms include:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Hyperactivity
- Difficulty concentrating or inattentiveness which can result in poor school performance
- Behavior and emotional problems (irritability, aggressiveness, being disruptive or moody)
- Bedwetting
If you are not sure if your child is snoring or has true sleep apnea, it is very important to have a consultation with a pediatric otolaryngologist.
Children who snore should always be evaluated to ensure they do not have a more serious condition.
Are there health risks associated with obstructive sleep apnea?
Even in children, there may be serious health risks associated with obstructive sleep apnea. These include:
- Elevated blood pressure and cardiovascular problems
- Delayed growth
- Obesity
What are the treatment options?
Depending on the assessment of your pediatric otolaryngologist, several options may be considered. These include:
- Nasal spray
- Surgery- tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy, etc
To learn more about Dr. Belinda Mantle and Pediatric ENT care, visit: http://ohni.org/pediatrics/