- Shingles and Facial Nerve Damage - May 1, 2014
- Tattoo Removal - October 23, 2013
- Folliculitis: Frequently Asked Questions - April 12, 2011
- Adenoids: Frequently Asked Questions - April 12, 2011
- Serum Injection - September 17, 2010
- Treatment of Acne and Rosacea - September 10, 2010
Doctor, my child snores a lot. What’s the problem?
Snoring is the sound of air caused by air passing through the nose and vibrating across the soft palate. The commonest cause of snoring in kids is enlarged adenoids.
What are adenoids?
Adenoids are tonsil like tissues at the back of the nose, which when enlarged obstruct the back of the nasal passages, and interfere with air flowing through the nose.
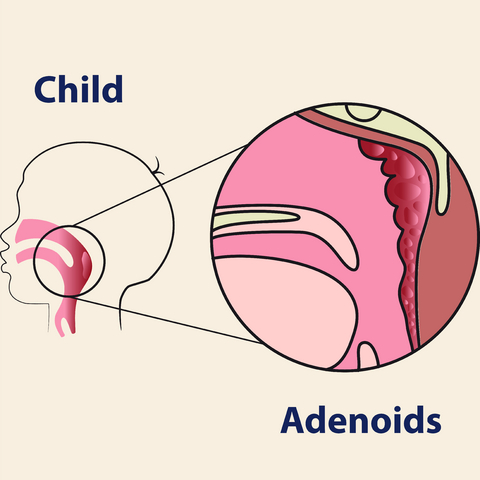
Do we all have adenoids?
Yes. However unlike the tonsils they eventually disappear at puberty.
What makes adenoids enlarge?
The commonest causes are recurrent infections and allergy.
So what if my child has enlarged adenoids? How does it affect their health?
If the adenoids are enlarged then the child becomes a mouth breather and as the jaw is developing they can develop an overbite which may require braces in the future.
Can enlarged adenoids affect my child’s hearing?
If the adenoids are large enough to obstruct the opening of the eustacian tubes which are located in the area of the adenoids, it interferes with the ventilation of the middle ears and can result in fluid collecting in the middle ears. This will affect the child’s hearing.
If the fluid does not respond to treatment, in addition to the child needing tubes (grommets), they may also require the adenoids to be removed.
How are enlarged adenoids diagnosed?
There are 3 ways to determine this.
– If the child snores the chances of having enlarged adenoids are very high.
– The adenoids can also be evaluated by passing an endoscope through the nose and visualizing the adenoids. Not an easy task for the doctor, but doable.
– An x-ray of the neck will also confirm the presence of enlarged adenoids.
Do the enlarged adenoids need to be removed?
It depends on whether or not they are enlarged as part of an acute infection in which case, no. Antibiotics will shrink them. It is only an issue if they are chronically enlarged and cause difficulty breathing, or recurrent sinus and ear infections.
The upper airway is like a drain, and when a drain is clogged things back up and cause problems .In this case it is the adenoids and unclogging the drai by removing the enlarged adenoid will correct the problem.
How are they removed?
Adenoids are removed in an operating room under general anesthesia.
Do the tonsils also need to be removed at the same time?
Not necessarily. Only if they are contributing to the obstruction or they are chronically infected.
Is an adenoidectomy (removal of the adenoids) a painful procedure?
Not really. Unlike a tonsillectomy that is painful, the pain is quite mild, and there are no food restrictions.
If my child needs grommets, can both procedures be done together?
Yes.
Will my child have to stay in the hospital?
No. It is done as an out-patient procedure. After the child leaves the hospital they generally go home and have a good sleep and when they wake up in most cases it is like nothing has happened.
What are the risks?
Bleeding is the main potential risk and that is why we stop all medications that can affect clotting two weeks before the surgery.
Can adenoids re-grow?
Tonsils are like a grape and have a skin (capsule) around them. Once removed, they can never re-grow. Adenoids on the other hand are like an iceberg, and can only be removed down to the surface of the tissues, and can re-grow. However the incidence is very low.
To learn more about Dr. Raphael Nach or adenoids, visit: http://www.ohni.org/



