- India Medical Mission 2018 - November 1, 2018
- Sleep Disorders: Sleep Apnea and Upper Stimulation Therapy - August 25, 2015
- The Naked Vocalist Podcast Featuring Dr. Reena Gupta - May 27, 2015
- New Therapy for Sleep Apnea – First Sleep Pacemaker placed in California at Osborne Head and Neck Institute. - December 12, 2014
- Boxer’s Ear: Can your ear explode? - December 12, 2014
- Nose Picking (Rhinotillexis) and Septal Perforations: Why I should stop picking my nose…? - November 24, 2014
- Deviated Septum and Septal Perforation - July 28, 2014
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Nasal Septal Perforation Repair - June 25, 2014
- Dr. Mantle recognized at the Beverly Hills Medical Science Academy Awards - May 8, 2014
- Commonly Misdiagnosed Pathologies: Arteriovenous Malformations - April 9, 2014
No. 3-ranked UFC fighter, Leslie Smith sustained a match-ending right cross to the side of her head in a bout against contender Jessica Eye. The 125lb fighter was forced to stop the fight when a hematoma in her left ear violently ruptured after a direct blow from her opponent. Leslie had been draining a preexisting auricular hematoma multiple times a day leading up to the fight. Smith’s ear continued to fill with blood during the fight and ultimately burst under the pressure of a well placed blow to the ear. Much to Leslie’s dismay, the fight was stopped shortly thereafter. It was definitely the right call, which Leslie also admitted herself after watching the video after the fight concluded. This is one tough fighter, though she may have placed herself under unnecessary risk.

Unfortunately scarred, gnarled, and deformed ears have become a modern day sign of a warrior. Media outlets incorrectly described the injury as cauliflower ear, so we thought we would spend some time highlighting the differences between cauliflower ear and auricular hematomas. Understanding how to prevent both injuries can help to prevent permanent deformity.
What is an auricular hematoma? An auricular hematoma is a swollen and tender collection of blood trapped between the skin and cartilage of the ear. The normal contours of the cartilage are no longer easily identifiable and the ear may feel like a water ballon.
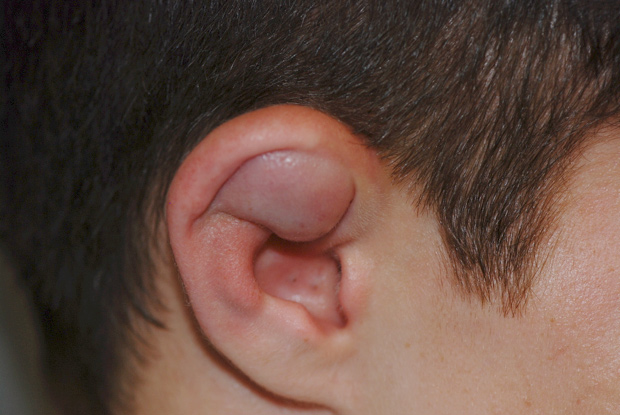
When should I see a doctor? If an auricular hematoma is not drained and splinted early it can lead to a condition called cauliflower ear.
What is cauliflower ear? Cauliflower ear is the permanent change to the shape of the ear. It occurs when an auricular hematoma is not drained appropriately. Prolonged pressure from an auricular hematoma causes permanent damage to the cartilage of the ear and leads to scarring and disfigurement of the ear’s framework. A cauliflower ear is much harder to treat and difficult to reverse. As such the best treatment for cauliflower ear is prevention with immediate and appropriate treatment of auricular hematoma.
What are my treatment options? Needle drainage of auricular hematomas is not the appropriate treatment to prevent a cauliflower ear. The typical result, after needle drainage of an auricular hematoma is that the blood simply re-accumulates. Furthermore, the needle can only remove unclotted blood and fluid. Needles cannot remove larger blood clots that have already formed. As such, needle drainage of an auricular hematoma is not the appropriate treatment. Proper treatment of an auricular hematoma requires making a small incision on the skin of the ear; the hematoma is then drained completely. A pressure dressing is then applied for 3-5 days so that another hematoma does not re-accumulate under the skin. After the appropriate time has passed the dressing is removed. Headgear should then be worn for 2-3 months to protect the ear as it continues to heal. In cases of preexisting cauliflower ear, the ear can sometimes be sculpted to look like a normal ear after the fighter has retired.
To learn more about Dr. Ryan Osborne or auricular hematoma treatment, visit: www.facialtraumamd.com.



