- What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)? - September 13, 2012
Question:
“My doctor told me I might be at risk for sleep apnea because I snore. I’m a 42 year old non-smoker with a normal body weight so I was really surprised to hear this. Is it possible that I have sleep apnea? What exactly is sleep apnea?
Discussion:
Sleep apnea originates from the Greek word apnea, meaning “want of breath.” This is fitting because sleep hinders the body’s intake of its most valuable resource: oxygen.
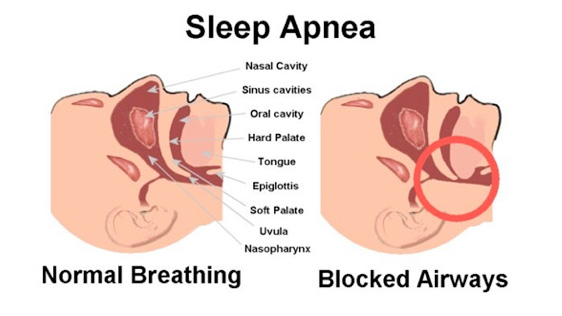
What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious condition that affects an estimated 1 in every 15 people in America. This disorder affects breathing during sleep, causing periods where the patient is unable to take a breath. These cessations of breathing can last anywhere from 10 to 30 seconds, meaning that for that time, the patient is essentially holding their breath!
There are three different types of sleep apnea:
- Central
- Obstructive
- Mixed
Of these, obstructive sleep apnea is the most common. There can be many causes for obstructive sleep apnea such as having large tonsils, a large tongue, a small jaw, or a nasal obstruction due to a deviated septum, allergies, or sinus problems.
What are the symptoms of sleep apnea?
One reason why sleep apnea is hard to diagnose is because the most prominent symptoms occur during sleep. Therefore, ask a bed partner to observe your sleeping habits or record yourself sleeping. Major symptoms include:
- loud and chronic snoring
- choking, snorting, or gasping during sleep
- long pauses in breathing
- daytime fatigue
- difficulty concentrating
- chronic headaches
What are the risks of sleep apnea?
In a night, these periods without oxygen take a toll on the body. The seriousness of this disorder is due to the multiple possible effects a lack of oxygen has on the body. A patient with obstructive sleep apnea is four times more likely to have a stroke and three times more likely to have heart disease. Other possible risks include:
- high blood pressure
- fatigue and poor performance in everyday activities (i.e., work ,driving, etc)
- death
Who gets sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is not age- or gender-specific. This means that anyone, young or old, male or female, can suffer. Newborns can be diagnosed, as can the elderly. For this reason, it is important to understand the symptoms to know if you might be suffering too.
However, there are certain risk factors:
- male gender
- overweight or obese
- family history of sleep apnea
It is important to recognize that even those who don’t fit these risks may suffer from sleep apnea. This includes the young, slim female patient who asked the question above.
What are the treatment options?
There are many different treatment options for obstructive sleep apnea. You must work with your ENT doctor to find the one that is best for you. During this consultation, you may be offered:
- continuous positive airway pressure mask (CPAP mask)
- tonsillectomy: removes the tonsils that are obstructing the airway
- weight loss support
- nasal decongestants
- nasal surgery
- uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) surgery: removes the tonsils, part of the soft palate and the uvula to open the oral airway
Obstructive sleep apnea usually goes undiagnosed and is just thought of as having “really bad snoring” or “insomnia.” However, it is a disease of great seriousness that should be diagnosed and treated if the signs are seen.
Key Points:
Definition: Sleep apnea is the cessation (stoppage) of breathing during sleep.
Symptoms: Loud and chronic snoring, choking, snorting, or gasping during sleep, long pauses in breathing, and daytime fatigue are all symptoms of sleep apnea.
Treatment: Sleep apnea must be treated aggressively to prevent complications and major health risks. Medical, minimally-invasive, and surgical options are selected based on patient tolerance and severity of sleep apnea.
Read patient stories about Dr. Lorraine Williams-Smith of the Osborne Head & Neck Institute.

To learn more about obstructive sleep apnea and other procedures offered at the internationally renowned Osborne Head and Neck Institute visit our website at: http://www.ohni.org
